TLS sessions
Concept
Applicative level communication in a TCP session may be enciphered using TLS.
TLS is well described in Wikipedia.
Spider is able to capture TLS secrets used to encrypt and decrypt the TLS records in a TCP session.
These secrets are used in parsing services to decipher the encrypted content before parsing the applicative protocol.
This is managed completely behind the scenes, and the TLS session information is not stored in Spider.
Should you want to see, study or debug a TLS session, you may do it in the TCP content tab. As show below.
TLS secrets capture and link
TLS secrets are captured by Gociphers agents and then linked to their related TCP session.
You may find them in the TCP session resource:

- The
*Secret,clientRandom,serverRandom,cipher.nameandtlsVersionare the values captured from OpenSSL memory. - The
*Keyand*Ivare the keys and crypto initialisation vectors derived from the secrets in Spider backend. - The latter are used to decrypt the TLS records and content
Analysing the TLS session
The TLS session is best described as a diagram (from Wikipedia):
You may study the handshake of the TLS session in TCP content tab of the TCP session:
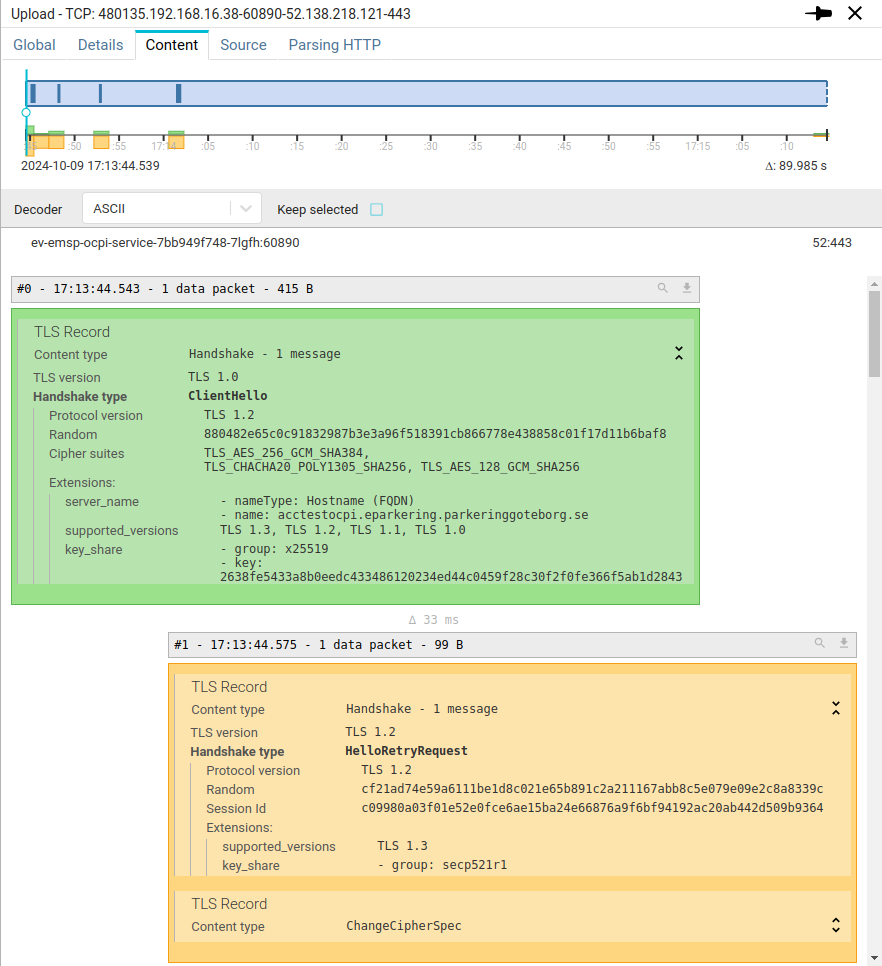
Spider parses the TLS records to extract the most relevant information allowing to understand and even debug the handshake. Encrypted TLS records are decrypting live and parsed the same way, while keeping the structure of the messages.
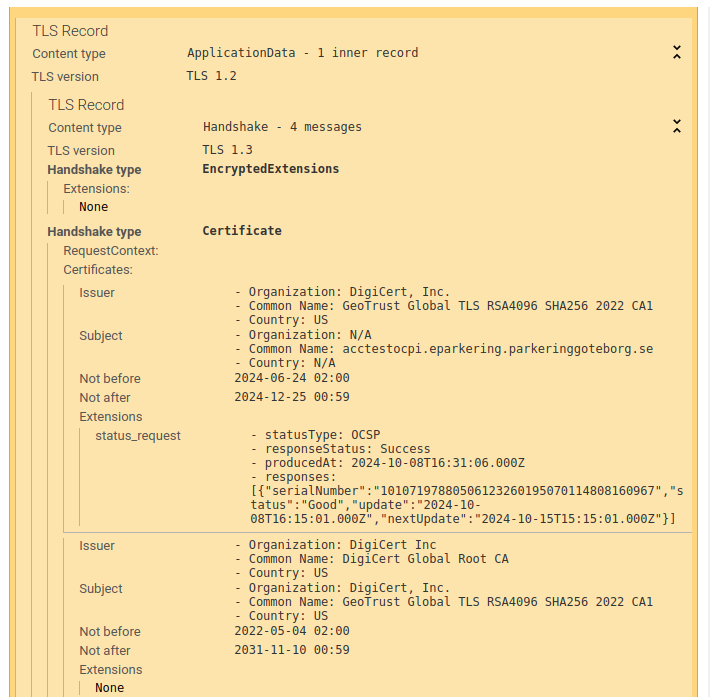
An encrypted handshake message may then include any Handshake records inside it:
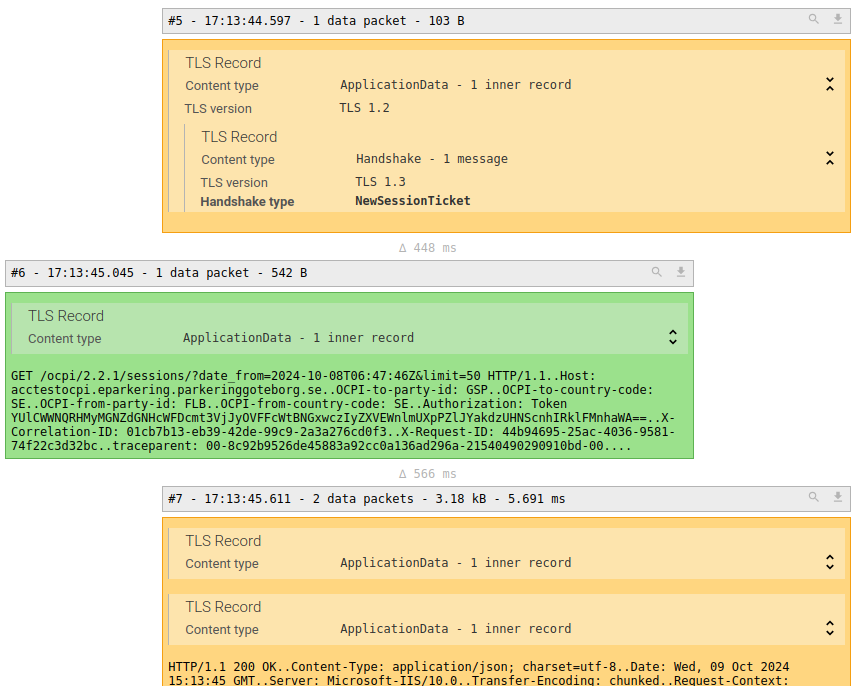
Application data records are represented with their aggregated deciphered payload below:
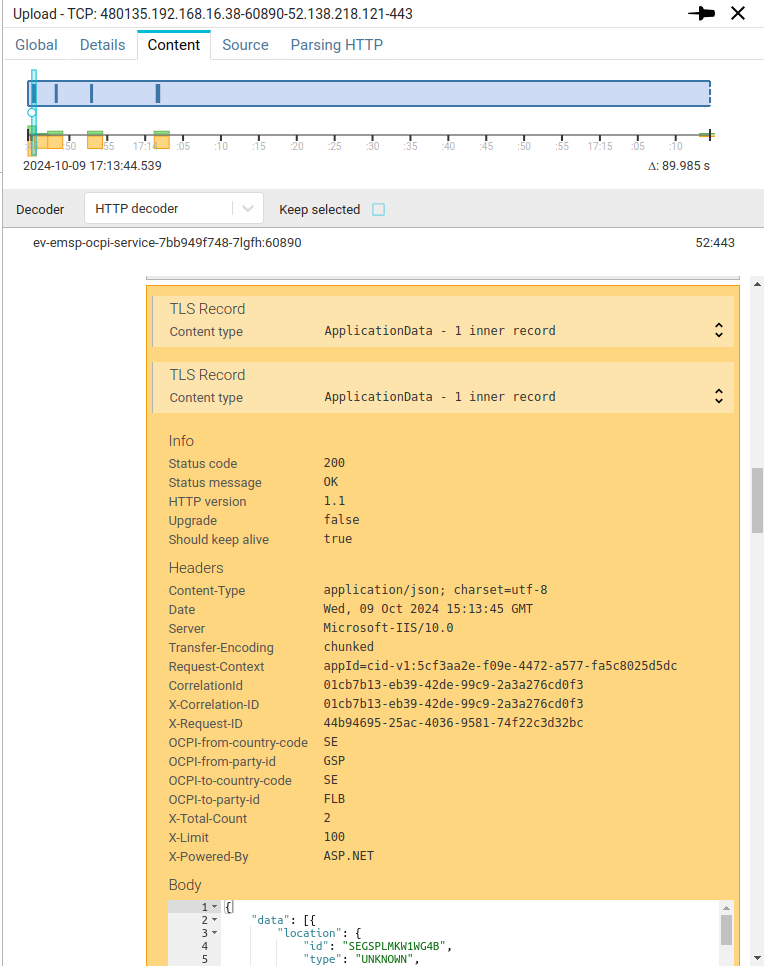
You may then apply the TCP content decoder plugins to decode the deciphered data:
- HTTP
- Redis
- MQTT
- ... and any other available plugin
Your TLS communications have no secret for you anymore 😍
Security concerns
Do decrypt TLS sessions, Spider does not hack the session, nor perform brute force.
It extracts TLS secrets from OpenSSL memory using eBPF kernel plugin technology.
To be able to do it, you need to give Spider high level permissions on your Linux hosts.
Make sure that you are allowed to do it!
Technology
Concept
Spider uses eBPF technology to capture OpenSSL secrets.
Spider loads the binary of OpenSSL library used - or of the application that statically linked OpenSSL -
to determine OpenSSL version.
Then it attaches eBPF probes to OpenSSL libraries functions to fetch the TLS secrets when they are called.
Spider may capture secrets from applications running on a Host - physical or virtual machine, but it also can
capture secrets from applications running in containers, by hooking in their kernel namespaces.
To perform this, the Gociphers Kubernetes daemonset uses wide permissions.
This may raise issues on your security tools, but this is required to use this feature.
Supported Kernels
Linux kernels with minimum version of 4.18
Supported TLS libraries
Below are the list of TLS libraries and currently supported ones
| Library | Description | Supported | Versions |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenSSL | Most used Opensource TLS library | ✅ | 1.1.1a -> 3.3.x |
| QuicTLS | OpenSSL fork managing QUIC protocol, statically linked to many versions of Node.js binary | ✅ | 3.0 -> 3.1.x |
| BoringSSL | OpenSSL fork developed by Google, tailored for their internal needs. It is utilized in various Google products and services. | ||
| LibreSSL | OpenSSL fork created by the OpenBSD Project, focusing on code simplification and security enhancements. | ||
| GnuTLS | An open-source TLS library written in C, offering a comprehensive API for secure communications. | ||
| crypto/tls | Go standard TLS library. | ||
| Network Security Services (NSS) | Developed by Mozilla, AOL, Red Hat, Sun, Oracle, Google, and others, NSS is a set of libraries designed to support cross-platform development of security-enabled client and server applications. | ||
| Mbed TLS | Formerly known as PolarSSL, this library is designed for embedded systems and is developed by Arm. | ||
| Bouncy Castle | A collection of APIs used in cryptography, including TLS implementations for Java and C#. | ||
| Rustls | A modern TLS library written in Rust, emphasizing safety and performance. | ||
| s2n | A TLS implementation developed by Amazon, designed to be small and fast, suitable for use in their cloud services. |
And other less known SSL libraries
Supported protocols
| Component | Description | TLS 1.1 | TLS 1.2 | TLS 1.3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gocipher | Captures secrets | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Analysis UI | Decrypt TLS session in the Browser | ✅ | ✅ | |
| Web Write | Decrypt TLS session and parses HTTP communications | ✅ | ✅ |
TLS 1.1 and earlier are deprecated and should not be used anymore.
If you ever need Spider to decipher those, contact me directly.
Supported Ciphers
- TLS 1.2 includes hundreds of cipher suites!
- TLS 1.3 includes only 5 ciphers.
Spider only supports the default OpenSSL active ciphers at the time of writing.
They can be listed with these commands:
openssl ciphers -tls1_2 -stdname -s -Vopenssl ciphers -tls1_3 -stdname -s -V
Also, legacy CBC ciphers have a variation in ciphering depending on selected extensions:
Mac-Then-Encrypt- MAC is done on plain content before encryptionEncrypt-Then-Mac- MAC is done on encrypted content (more secured)
Spider supports both 💪.
TLS 1.3 ciphers
| Ciphers | Tested | Mozilla evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 | ✅ | Modern |
| TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 | ✅ | Modern |
| TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256 | ✅ | Modern |
| TLS_AES_128_CCM_SHA256 | ⛔ | |
| TLS_AES_128_CCM_8_SHA256 | ⛔ |
TLS 1.2 ciphers
| Ciphers | Tested | Mozilla evaluation |
|---|---|---|
| TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA | ✅ | ⛔ |
| TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 | ✅ | Old |
| TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 | ��✅ | Intermediate |
| TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA | ✅ | ⛔ |
| TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 | ✅ | Old |
| TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 | ✅ | Intermediate |
| TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256 | Intermediate | |
| TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA | ✅ | Old |
| TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 | ✅ | Old |
| TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 | ✅ | Intermediate |
| TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA | ✅ | Old |
| TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 | Old | |
| TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 | ✅ | Intermediate |
| TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256 | ✅ | Intermediate |
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA | ✅ | Old |
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 | ✅ | Old |
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 | ✅ | Intermediate |
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA | ✅ | Old |
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384 | ✅ | Old |
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 | ✅ | Intermediate |
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256 | ✅ | Intermediate |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA | ✅ | Old |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 | Old | |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 | ✅ | Old |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA | ✅ | Old |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 | Old | |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 | ✅ | Old |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA | Old |
Supported TLS extensions having effect on decryption
Extensions that affects deciphering:
| Extension | Code | TLS | Deprecated | Supported |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TLS Compression | ⛔ | |||
| Record size limit | 28 | ⛔ | ||
| Encrypt-then-MAC | 22 | 1.2 | ✅ | |
| Pre-Shared Key | 41 | 1.2 1.3 |
Extensions that strengthen key derivation by adding extra input:
| Extension | Code | TLS | Deprecated | Supported |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Opaque PRF Inputs | 16 | ⛔ | ||
| Extended Master Key | 23 | 1.2 | ||
| Early data | 42 | 1.3 |
Supported applications languages whose capture is possible
Spider can capture secrets from applications dynamically linked to a supported TLS library.
This covers a wide range of applications coded with numerous programming languages:
- C, C++
- Java
- Node.js
- PHP
- Python
- .Net framework
- ...
Spider can also capture secrets of Node.js applications statically linked to OpenSSL.
Limitations
With current state of development:
- As TLS is stateful,
- Spider must capture the first packets of the session to decrypt TLS.
- TCP content tab needs to have the first packets in its view to decrypt TLS.
- Moving the blue cursor on the TCP timeline breaks decrypting feature.
- Except if you have loaded all parts first.
Not tested
- TLS key renewal capture has not been tested (not used anywhere in our systems)
- TLS sessions using session reuse or early data handshake messages have not been tested either.
- But these features are often disabled in production due to security concerns.